Types of Vaccine and Manufcturers
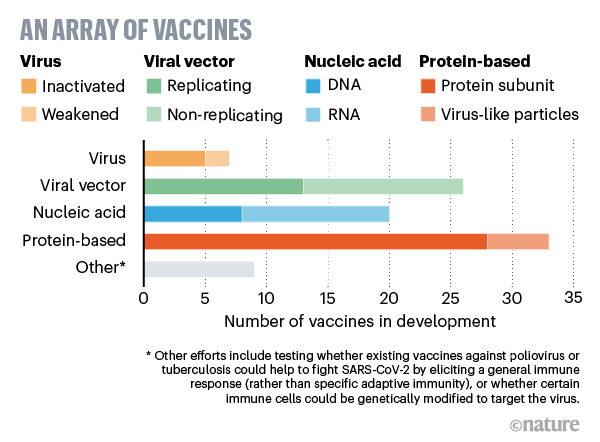
Virus vaccines
At least seven teams are developing vaccines using the virus itself, in a weakened or inactivated form. Many existing vaccines are made in this way, such as those against measles and polio, but they require extensive safety testing. Sinovac Biotech in Beijing has started to test an inactivated version of SARS-CoV-2 in humans.
Attenuated SARS-CoV-2 virus vaccine candidates are being developed by:
- US company Codagenix and the Serum Institute of India
- Indian Immunologicals Ltd and Australia’s Griffith University.
- Wuhan Institute of Biological Products
- Sinovac Biotech are currently in phase I/II clinical trials in China.
-
Valneva is an inactivated whole virus vaccine
Viral-vector vaccines
Around 25 groups say they are working on viral-vector vaccines. A virus such as measles or adenovirus is genetically engineered so that it can produce coronavirus proteins in the body. These viruses are weakened so they cannot cause disease. There are two types: those that can still replicate within cells and those that cannot because key genes have been disabled.
- Jenner Institute and the Oxford Vaccine Group.
- Institut Pasteur in France
- University of Pittsburgh in the US
- Themis Bioscience a Merck subsidiary in Austria expects to begin testing their measles virus-vectored candidate in animals this month.
- Cansino non-replicating adenovirus type-5 (Ad5)-vectored COVID-19 vaccine
- Johnson and Johnson uses a specially modified virus, called Ad26
Nucleic-acid vaccines
At least 20 teams are aiming to use genetic instructions (in the form of DNA or RNA) for a coronavirus protein that prompts an immune response. The nucleic acid is inserted into human cells, which then churn out copies of the virus protein; most of these vaccines encode the virus’s spike protein.
RNA Type
- Moderna Therapeutics began its phase I trial in the US in March
- Germany’s BioNTech Pfiser began their combined phase I/II trial at the end of April.
- US-based Pfizer began their combined phase I/II trial at the end of April.
- A team at Imperial College London is also among those doing pre-clinical testing of RNA vaccine candidates.
- CureVac’s product uses nucleotides without chemical modifications in the mRNA
DNA Type
- US-based Inovio Pharmaceuticals, working with four other companies in the US, China and Germany, recently began a phase I clinical trial of its SARS-CoV-2 DNA vaccine candidate.
- UK-based Scancell, working with scientists at the University of Nottingham, is also testing a DNA vaccine candidate, with development currently in the pre-clinical stage.
- Inovio US Company
Protein-based vaccines
Many researchers want to inject coronavirus proteins directly into the body. Fragments of proteins or protein shells that mimic the coronavirus’s outer coat can also be used.
- VIDO-InterVac at the University of Saskatchewan in Canada
- ExpreSion Biotechnologies in Denmark is currently part of an EU-funded consortium to develop a VLP vaccine candidate using fruit flies to produce recombinant proteins,
- Medicago Inc in the US aims to start phase I trials of a plant-produced VLP vaccine by the summer.
- Novavax Nano particle vaccine
- Clover Biopharmaceuticals/GSK uses a protein-based coronavirus vaccine candidate (COVID-19 S-Trimer).
A List of Vaccine Manufactures and their progress (regularly updated)
A graphical guide to Coronavirus vaccines the 4 main types explained in Nature with diagrams.
A detailed guide of the Coronavirus vaccines including the subtypes with diagrams.
Vaccines highlighted in this way have been acquired by UK government. Note there is one from each vaccine category.
As of 14th August Johnson and Johnson’s Janssen vaccine a viral vector vaccine and the Novavax protein based vaccine have been added to the UK governments list of vaccines taking the the different vaccines of the 4 types of vaccine to 6 and the total number and the total number of doses up by 90 million doses to 340 million doses.
The purchase of the vaccines is discussed in this article.